Basic Attitude and Targets
The Nippon Shinyaku Group has identified “Strengthening efforts to protect the global environment” as one of its key material issues and is actively addressing climate change. We are working to reduce CO2 emissions by cutting energy consumption and carrying out other measures, taking into account the impacts of climate change. As part of these efforts, we have been promoting the switch to renewable energy since FY2021. As a result, in FY2024, the share of renewable energy-derived electricity reached 48% of the Group’s total electricity consumption. Going forward, we will promote the further expansion of renewable energy, including at our production sites.
The Nippon Shinyaku Group has established science-based CO2 reduction targets. These targets were certified by the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) in January 2024. We have set a short-term target of 9,266 t-CO2 for FY2025 (a 21% reduction compared to the base year of FY2020), a medium-term target of 6,088 t-CO2 for FY2030 (a 42% reduction compared to the base year of FY2020), and a long-term target of achievingnet-zero CO2 emissions by FY2050. Toward achieving these targets, we will steadily advance our efforts.
The Nippon Shinyaku Group will continue to actively implement climate change measures to help protect the global environment and strive toward the realization of a sustainable society.
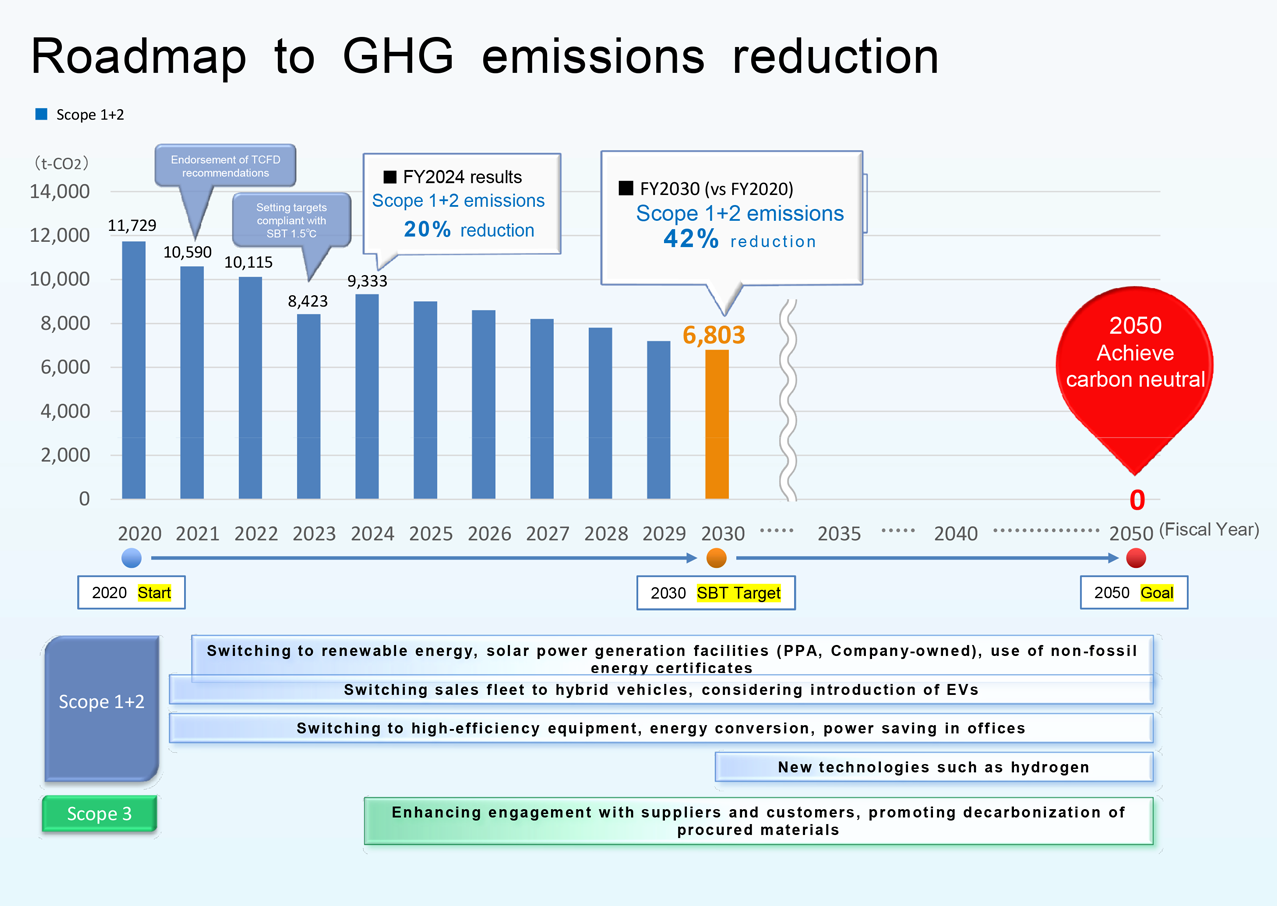
Roadmap to GHG emissions reduction
■Rate of Change-Over to Electricity Derived From Renewable Energy Sources
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% | 17% | 27% | 53% | 48% |
Reducing CO2 emissions and Energy Consumption
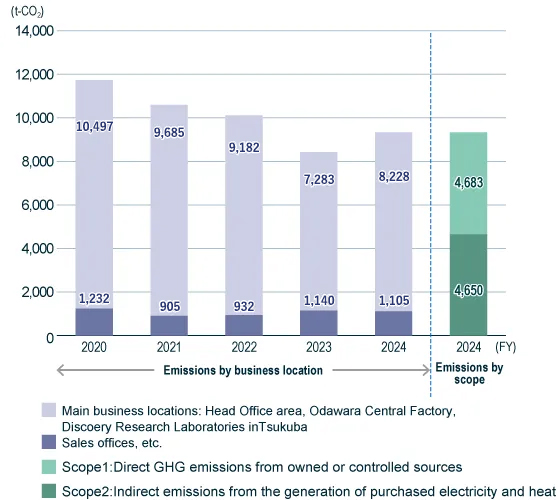
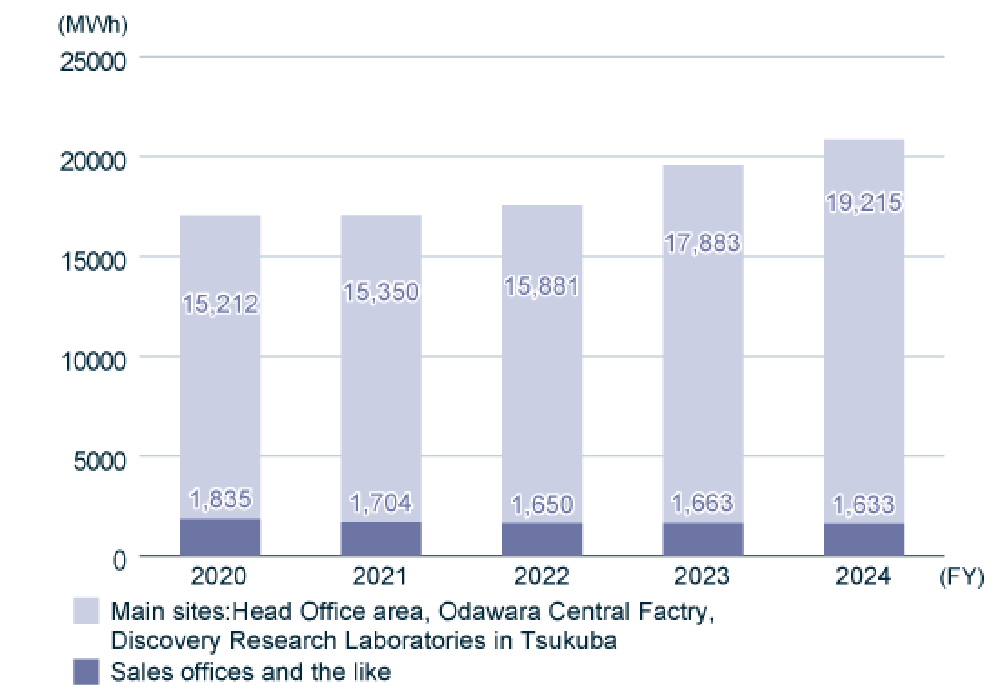
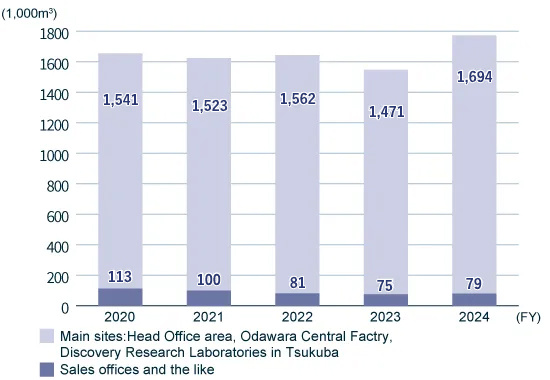
In FY2024, Nippon Shinyaku Group’s Scope 1 and 2 CO2 emissions totaled 9,333 t-CO2, representing a 20.4% reduction compared to the FY2020 benchmark. Total energy consumption was 44,845 MWh, with electricity usage increasing by 22.3% and gas usage by 7.2% from FY2020 levels.
Although energy consumption increased compared to FY2020, Scope 1 and 2 CO₂ emissions decreased due to the introduction of renewable energy starting in FY2021.
To achieve net-zero emissions by FY2050, we will continue our efforts beyond equipment replacement by reviewing operating hours, temperature settings, and other operational parameters. We also plan to expand our use of renewable energy, including the installation of solar power generation systems.
CO2 emissions
Breakdown of energy consumption by source
●Electricity
●Town gas
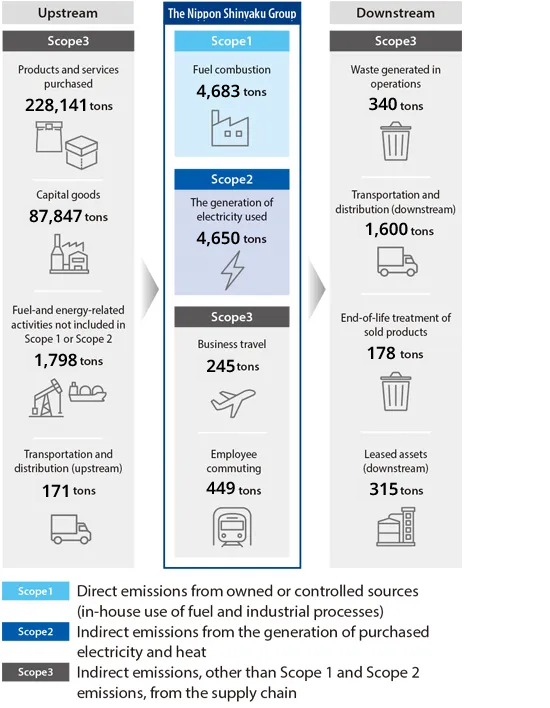
Supply chain emissions (FY2024 results)
1. Utilization of renewable energy
Aiming to achieve net-zero emissions by FY2050, the Nippon Shinyaku Group will reduce CO2 emissions to 6,803 t-CO2 by FY2030 (a 42% reduction compared to the base year of FY2020).
In April 2021, we began switching the electricity consumed in our Head Office area to renewable energy sources, and in FY2023, all electricity consumed in the Head Office area was converted to renewable energy. In November 2022, we began switching to hydropower-derived electricity at the Odawara Central Factory. We also installed solar power generation facilities at the Discovery Research Laboratories in Tsukuba in 2022, at the Odawara Central Factory in 2023, and in the Head Office area and at Tajima Shokuhin Kogyo Co. Ltd. in 2024.
Through these initiatives, 48% of the Group’s total electricity consumption was converted to electricity derived from renewable energy sources in FY2024.
From FY2025 onward, as part of efforts to further expand the use of renewable energy, we are considering the purchase of FIT non-fossil certificates with tracking to convert our electricity consumption to renewable energy in real terms.
In FY2023, we discontinued the cogeneration system in our Head Office area, thereby reducing CO2 emissions generated by natural gas combustion.
2. Introducing hybrid company-owned vehilcle representatives
By introducing hybrid vehicles for our sales activities and encouraging employees to use public transportation in urban areas, we have implemented measures to more effectively address climate change and raise employee awareness.
Since FY2020, Nippon Shinyaku replaced all sales vehicles with hybrid models over a four-year period, except for those used in regions with heavy snowfall.
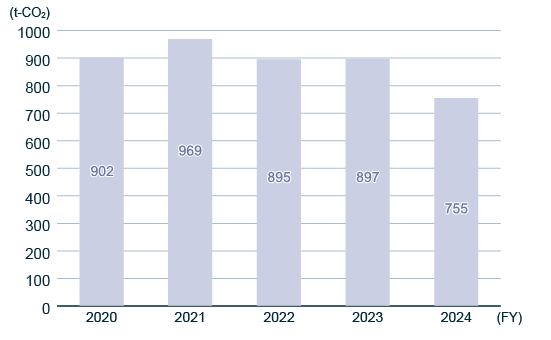
Yearly Trend of CO2 Emissions from Company Vehicles

3. Reducing energy consumption through equipment improvement
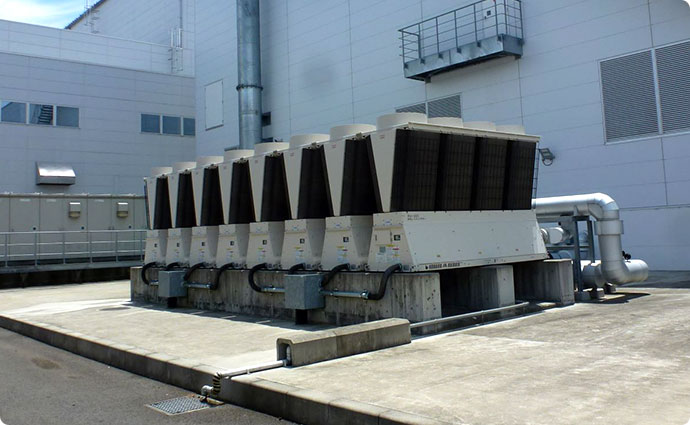
On the occasion of equipment renewal, we renew air-conditioning refrigerators, boilers, and total heat exchangers. We have also been gradually replacing conventional lighting equipment with LED equipment and installing motion detectors on lighting equipment. Through these measures, we aim to reduce CO2 emissions, thereby contributing to climate change alleviation.
At the Odawara Central Factory, we introduced highly efficient chillers at the time of the renewal of air-conditioning refrigerators. At the Tokyo Office, ice thermal storage equipment (*) was introduced to level off consumption peaks.
(* This shifts daytime power consumption for air conditioning to night time, with the use of ice heat stored in the thermal storage tank during the night.)

4. Energy conservation following the guidelines for saving electricity and energy
We are making company-wide power and energy-saving efforts, following the guidelines for saving electricity and energy drawn up by an in-house committee specifically established to promote conservation initiatives. Concrete company-wide power-saving measures range from appropriate indoor temperature settings to encouraging personnel to turn off all unnecessary lights and use stairways instead of elevators. We are also promoting energy-saving measures designed to fit closely to the flextime system and the decreased numbers of days employees work at the company workplaces.
Expanding initiatives
In addition to equipment renewal, equipment operating hours and temperature settings are also continuously reviewed to improve our energy-saving performance. In FY 2021, the introduction of renewable energy sources commenced. Initiatives involving the use of renewable energy, including the installation of solar power generators, will be further examined and implemented.
5. Participation in the FPMAJ Action Plan toward Low-carbon Society
Nippon Shinyaku participates in the Action Plan toward Low-carbon Society that the Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers’ Associations of Japan (FPMAJ) formulated at the request of Keidanren (the Japan Business Federation).
Nippon Shinyaku observes climate-change-related regulations imposed by the Japanese government under the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures. The company submits a report of its energy consumption, the progress of its efforts to achieve its energy-saving targets, and its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to the authorities every year.
In-house Awareness-raising Education
The importance and necessity of environmental protection are covered in a range of in-house training and educational programs, including intranet-based training programs. These programs contribute to raising and maintaining employees’ environmental awareness.







